Furnaces, heaters, and boilers burn fuel to produce heat. Achieving an intelligent balance of fuel and air will provide the most efficient combustion and highest cost savings. Efficient combustion also reduces emission of pollutants such as nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter.
Measuring the exhaust gas is an excellent way to optimize fuel and air input. A gas analyzer will enable you to measure the concentrations of various gases and adjust burners on a boiler to help achieve optimal combustion.
Detection process
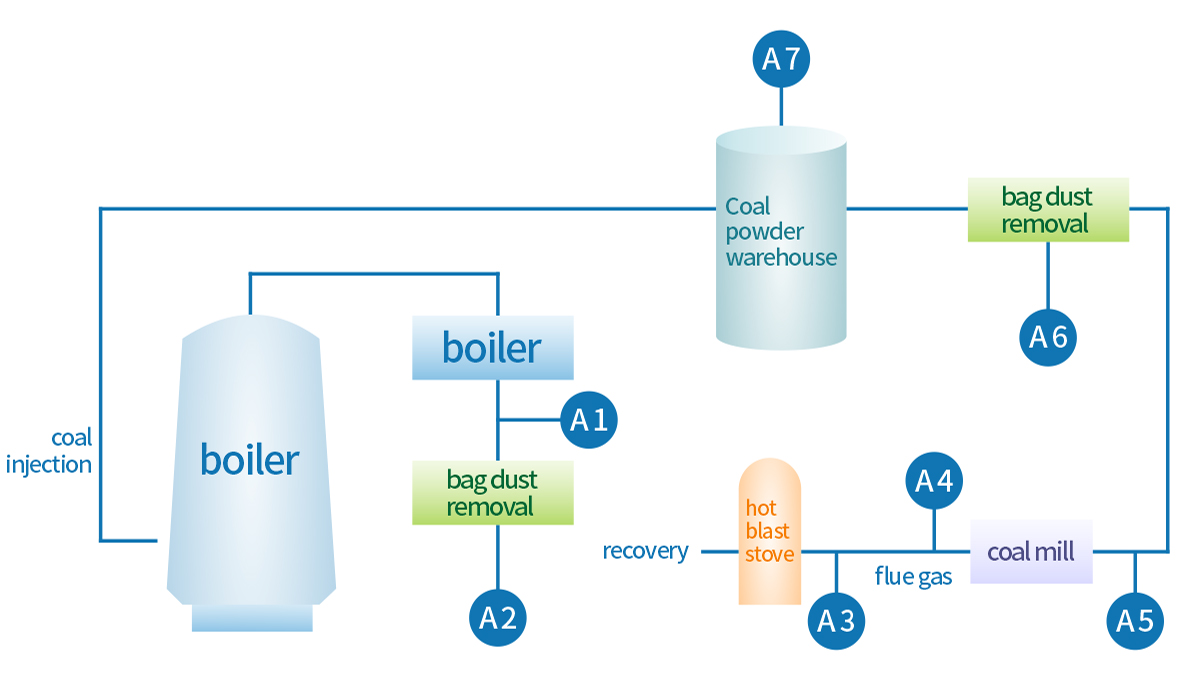
| Serial number | Detection point | Purpose | Measuring gas and range | Select probe | Instrument selection | System name and model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 |
After gravity dust collector |
Process optimization control |
cO:0-30% co2:0-40% CH4:0-1% 02:0-3% H2:0-5% |
|
Gasboard-3100 |
Blast furnace gas online analysis system Gasboard-9011 |
| A2 | After bag filter | |||||
| A3 | Hot blaststove outlet | Combustion control | o2:0-21% |
Blast furnace gas online
analysis system Gasboard-9031
|
||
| A4 | coal mill inlet | safety monitoring | o2:0-21% | |||
| A5 | coal mill outlet | o2:0-21% |
|
|||
| A6 | Bag filter outlet |
co:0-2000ppm o2:0-21% |
||||
| A7 | Pulverized coalbunker | co:0-2000ppm |
請(qǐng)聯(lián)系我們,獲取更多產(chǎn)品信息
 在線
在線 咨詢
咨詢 關(guān)注
關(guān)注